
A work led by researchers from CINE and RCGI advances the knowledge about the techniques that are capable of elucidating the carbon dioxide reduction reaction (CO2 RR) – a process that transforms this greenhouse gas into compounds of industrial utility and high added value. The study contributes to developing solutions that reduce carbon dioxide emissions to the atmosphere and, at the same time, take advantage of carbon dioxide as a […]

Perovskite solar cells can already compete with those made of silicon in terms of efficiency and cost. In addition, their lightness and flexibility make them attractive to some markets that the conventional technology cannot meet. However, these emerging devices cannot maintain their performance over time. This happens because perovskite films, that absorb sunlight and transform it into electricity, are note stable materials. They degrade when exposed to moisture, oxygen and […]
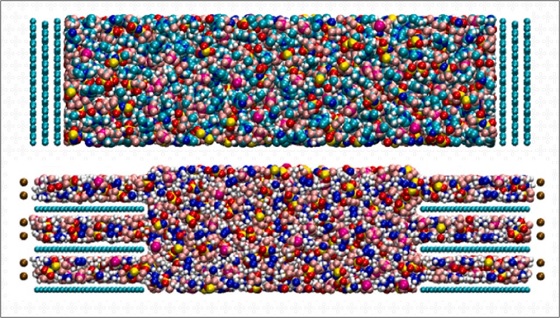
Supercapacitors stand out among energy storage technologies for their power (the speed at which they can charge and deliver energy) and for their lifespan (the number of charge and discharge cycles they can provide). However, these devices are limited in energy density, which is the amount of electricity they are able to store. In the context of CINE computational division, researchers from UNIFESP have joined the efforts of other scientists […]

A delegation from Shell visited CINE’s administrative headquarters and laboratories at UNICAMP on March 24th. Shell is a founding sponsor of CINE together with FAPESP. The meeting featured a presentation by the director of CINE, Prof. Ana Flávia Nogueira, on the results achieved over the three and a half years of the Centre’s existence. In addition, the delegation visited two laboratories linked to CINE’s Advanced Energy Storage program: the Battery […]
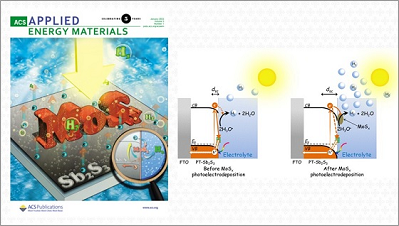
In an article featured on the cover of the journal ACS Applied Energy Materials, CINE researchers present a promising material for the generation of green hydrogen on a large scale. Hydrogen is a renewable fuel that does not generate carbon emissions during use. However, the hydrogen production methods available today are not environmentally friendly. One of the cleanest and most sustainable alternatives to obtain hydrogen is to split the water […]
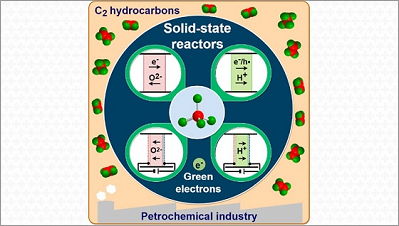
A study carried out within CINE’s Methane to Products (M2P) division addresses advances in the development of solid-state reactors, a technology that makes it possible to produce hydrocarbons in a cleaner and more sustainable way than the conventional one. With this technology, methane (a greenhouse gas) can be converted into more useful compounds through electrochemical reactions driven by renewable energies. Solid-state reactors (so called because they use solid electrolytes) are […]
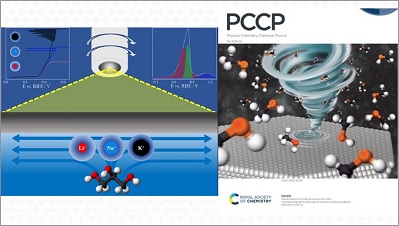
From the firewood used in the fireplace to the sugarcane ethanol that powers the car, biomass is a renewable and sustainable source of energy. In these two examples, biomass is burned, but there are more efficient ways than burning to harness the energy stored in plant and animal waste: electrochemical reactions, which involve the transformation of chemical energy into electrical energy and vice versa. In two papers published in 2021, […]

With the miniaturization of many types of devices, two-dimensional materials become increasingly relevant. However, preparing them on an industrial scale while maintaining their properties is often challenging. In a recently published article, members of CINE and collaborators present an important contribution to the search for methods that can enable the industrial production of these materials that are few atoms thick. The authors developed a fast, clean, scalable and simple method […]